Git
What is Git ?
A distributed version control system.
Why Git over SVN ?
- Github uses git. Most modern IT companies use git.
- Git is distributed, SVN is centralized. Git enables you to work and source control offline with your own repo.
- Most operations are done locally, so it’s fast.
How Git works
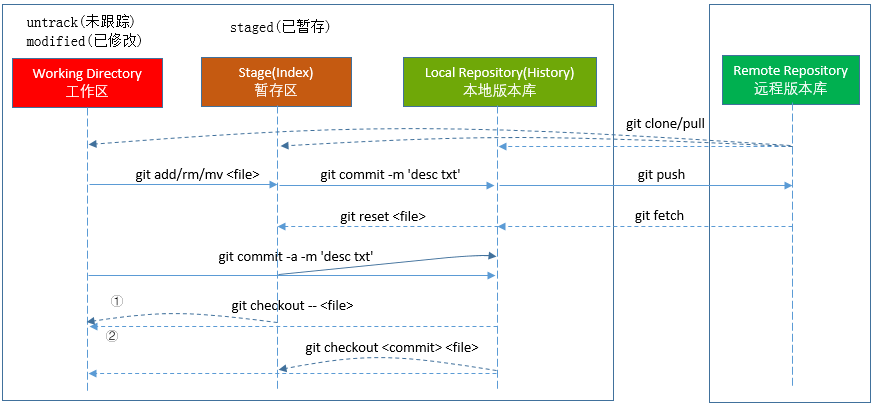
Git consists of 4 areas:
- Working Directory: Current working directory.
- Staging Area: Tracks and saves changes ready to commit.
- Local Repo: Repository on the disk.
- Remote Repo: Repository on the server.
Concepts
- HEAD: Current branch.
.gitignore file
Refs:
Patterns
| Pattern | Example matches | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| logs | logs logs/debug.log logs/latest/foo.bar build/logs build/logs/debug.log |
If you don’t append a slash, the pattern will match both files and the contents of directories with that name. In the example matches on the left, both directories and files named logs are ignored |
| logs/ | logs/debug.log logs/latest/foo.bar build/logs/foo.bar build/logs/latest/debug.log |
Appending a slash indicates the pattern is a directory. The entire contents of any directory in the repository matching that name – including all of its files and subdirectories – will be ignored |
| logs/* | logs/test.log(a file) logs/test(a directory) but not logs/bar/hello.c(a file) |
the asterisk in the pattern does not match “bar/hello.c” which has a slash in it. |
| logs/ !logs/important.log |
logs/debug.log logs/important.log |
Wait a minute! Shouldn’t logs/important.log be negated in the example on the left? Nope! Due to a performance-related quirk in Git, you can not negate a file that is ignored due to a pattern matching a directory |
| logs/**/debug.log | logs/debug.log logs/monday/debug.log logs/monday/pm/debug.log |
A double asterisk matches zero or more directories. |
| logs/*day/debug.log | logs/monday/debug.log logs/tuesday/debug.log but not logs/latest/debug.log |
Wildcards can be used in directory names as well. |
| logs/debug.log | logs/debug.log but notdebug.log build/logs/debug.log |
Patterns specifying a file in a particular directory are relative to the repository root. (You can prepend a slash if you like, but it doesn’t do anything special.) |
FAQ
What is HEAD in git ?
The HEAD in Git is the pointer to the current branch reference, which is in turn a pointer to the last commit you made or the last commit that was checked out into your working directory.
Git reset
Suppose we have a branch master with A/B/C commits:
- A - B - C (master)
reset --soft B: Moves pointer to B; changes staged; runcommitand will get a new commit as Creset --mixed B: Default. moves pointer to B; changes remain but unstaged; runaddandcommitand will get a new commit as Creset --hard B: Moves pointer to B; changes permanently reset; always runstatusto make sure changes can be discarded
Undo a commit
undo add: git reset
undo commit: git reset --hard HEAD~1 (moves to one commit before and --hard resets staging and working changes)
Links existing directory with remote repo
- In existing directory,
git init . git remote add origin <remote repo url>(originis a conventional name for remote repo)git push origin <local branch name>
What is a leading slash in .gitignore ?
The leading slash anchors the match to the root.
How can I ignore everything but one file in a directory ?
1 | git add -f Website\bin\Settings.json |
What is fast-forward ?
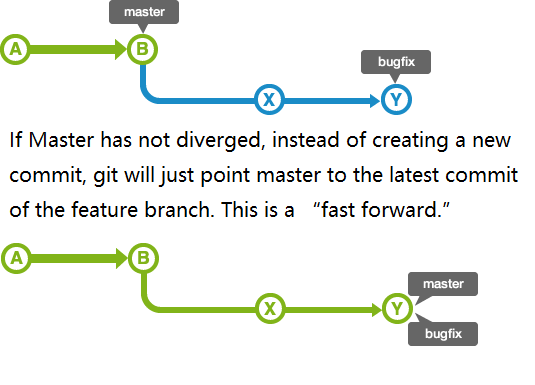
Git pull and git fetch
- Ref: Fetch vs pull
- Git pull: Incorporates changes from a remote repository into current branch and then fast-forward/merge current branch.
- Git fetch: If don’t want to fast-forward/merge, use this.
- pull = fetch + merge
Branches
git branch
Show all local branches, with current branch marked with an asterisk.1
2* master
Pagesgit branch -r
Show all remote branches.1
2origin/HEAD -> origin/master // Currently checked out branch, which is origin/master
origin/mastergit branch -a
List all branches.git branch newb
Create new branch named newb.git checkout newb
Switch to branch newb.git checkout -b newb
Shorthand forgit branch newbandgit checkout newb.git branch -d newb
Delete local branch newb.


