OAuth2.0
Refs
What is OAuth 2.0 ?
The industry-standard protocol for authorization.
This specification and its extensions are being developed within the IETF OAuth Working Group.
Authentication vs Authorization
Authentication verifies the identity of a user or service, and authorization determines their access rights. OAuth2.0 standards for Open Authorization.
Access token
An Access Token is a piece of data that represents the authorization to access resources on behalf of the end-user.
OAuth 2.0 doesn’t define a specific format for Access Tokens. However, in some contexts, the JSON Web Token (JWT) format is often used.
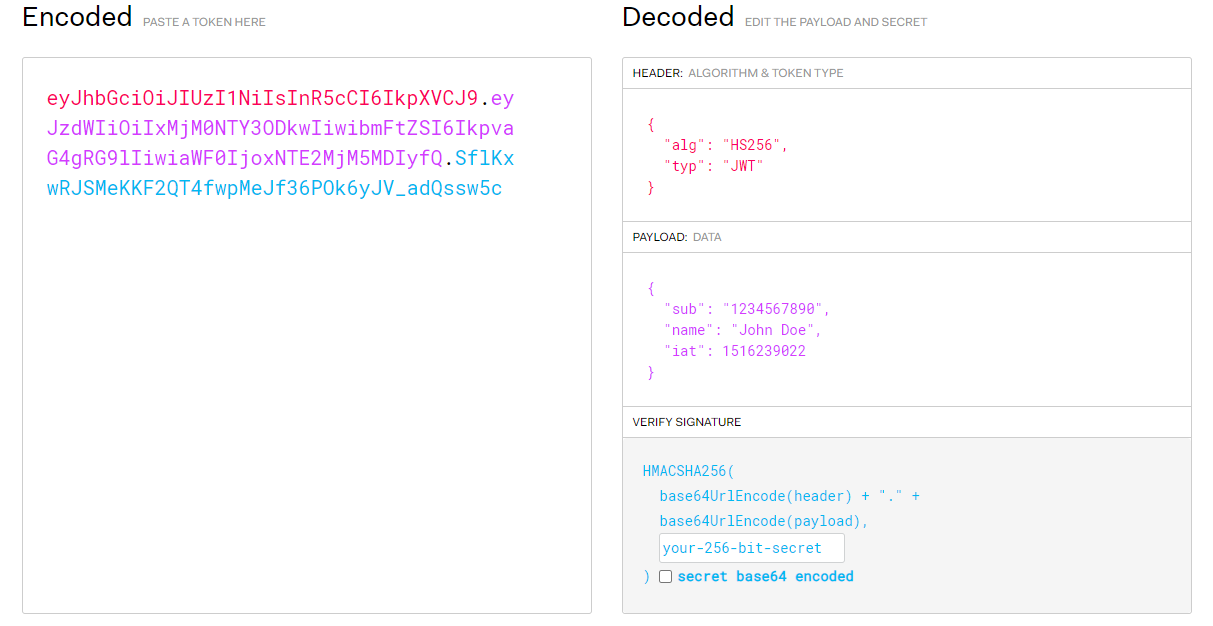
JWT
An open, industry standard RFC 7519 method for representing claims securely between two parties.
You can decode, verify and generate JWT.
Includes:
- Header: Algorithm and token type
- Payload: Data
- Signature: verifies data
Work modes
OAuth2.0 defines four work modes:
- Authorization code
- Implicit
- Password
- Client credentials
Authorization code is the most commonly used. We’ll introduce authorization code mode here.
Work flow
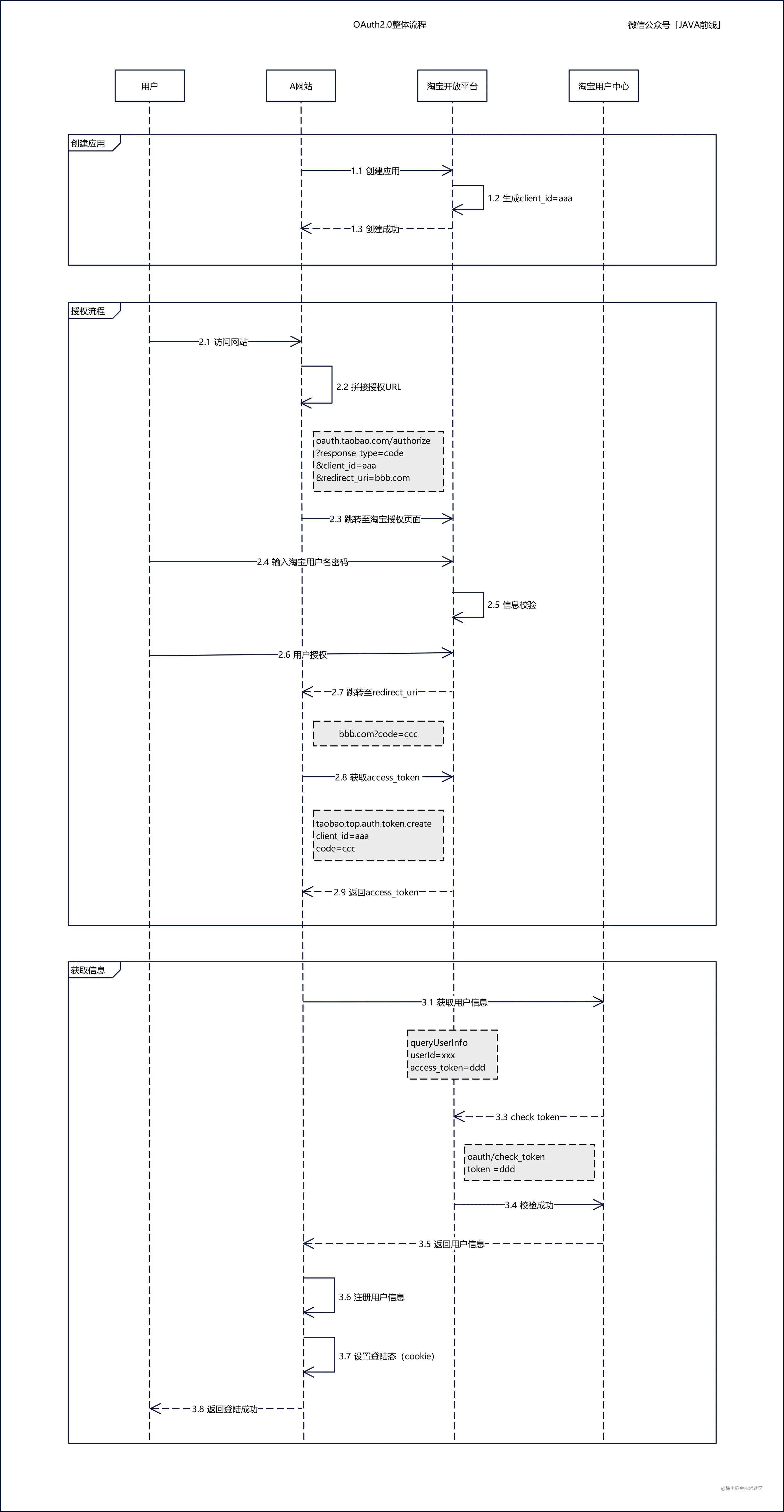
Example based on Taobao
Take Taobao as an example, if website A supports login with Taobao account, the process is follow:
- Registration. Website A registers itself on Taobao Open Platform, and Taobao Open Platform gives website A a
client_idas its unique identifier. - Authorization. When user login on website A with Taobao account, they are redirected to a URL concatenated by Taobao authorization page and website A’s address. User inputs their user name and password on the login page and gets redirected to website A after successful validation.
- Get token. Taobao Open platform gives website A a code, website A gets a token from Taobao Open platform with the code.
- Get user data. Website A gets user data from Taobao User Center with the token.
Work flow
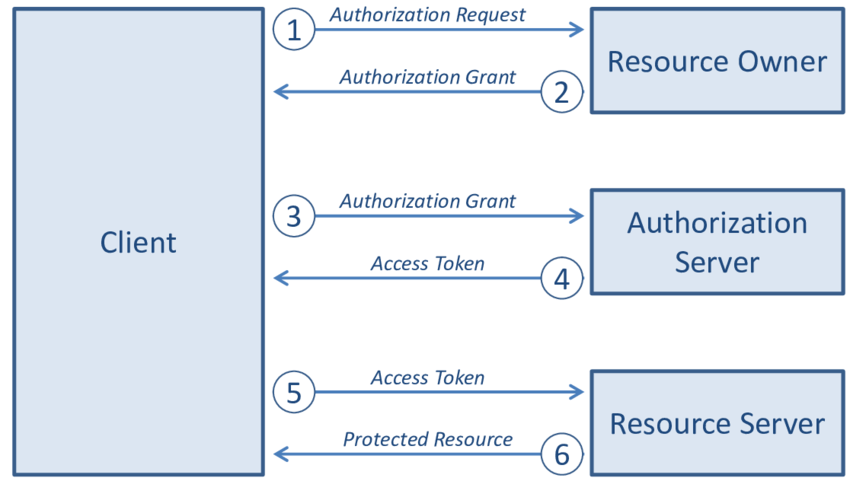
There are four roles in the work flow:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Resource Owner | Owner of resource, grants access to them. |
| Client | Requires access to resource, holds token. |
| Authorization Server | Receives requests from the Client for Access Tokens and issues them upon successful authentication and consent by the Resource Owner. |
| Resource Server | Accepts and validates an Access Token from the Client and returns the appropriate resources to it. |
The work flow is as below:
The Client requests authorization (authorization request) from the Authorization server, supplying the client id and secret to as identification; it also provides the scopes and an endpoint URI (redirect URI) to send the Access Token or the Authorization Code to.
The Authorization server authenticates the Client and verifies that the requested scopes are permitted.
The Resource owner interacts with the Authorization server to grant access.
The Authorization server redirects back to the Client with either an Authorization Code or Access Token, depending on the grant type, as it will be explained in the next section. A Refresh Token may also be returned.
With the Access Token, the Client requests access to the resource from the Resource server.


